Question: What is a email?
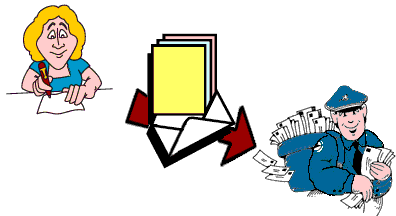
Answer: Electronic mail (e-mail) is a message sent electronically over the internet.
 |
|
Question: What is a email? |
|
Answer: Electronic mail (e-mail) is a message sent electronically over the internet. |
E-mail usually arrives at its destination in a matter of seconds.
Everybody that uses the internet has a unique e-mail address. E-mail addresses always have an ampersand (@) in them. This seperates the username from the location that their mail is stored. E-mail addresses are CaSe SeNsItIvE - so if someone reads you an e-mail address - ask about the capitals.
Just like the postman must be able to read the address to hand
deliver your regular mail, (snail mail - it's referred to on the internet,
because it take so long to get there) the e-mail address must be exact
in order for the computers to deliver it to your electronic mailbox.
| username | @ | mailserver |
|---|---|---|
| bwjames | @ | usd.edu |
Here are a few e-mail terms that you should be familiar with.
| address book | list of personal contact with their e-mail addresses |
| forward | sends the origional message on to someone else |
| reply | sends a e-mail to the sender of the message you are currently reading (sort of like someone sending you a self addressed stamped envelope) - this copies the senders e-mail address as well as the text from the message, you type your additional comments if necessary and send the message. |
| attachments | sends actual documents created with other programs along with (or attached to) your e-mail |
| CC
carbon copy |
sends the same message to several people (seperate their addresses with commas) |
| BC
blind carbon copy |
send message to several addresses without showing everyone all of the addresses (this is a good way to avoid those annoying messages that are 2 lines but 4 pages of addresses you really could care less about) |
| bounced | if a message has a invalid e-mail address it will be marked undeliverable and will bounce back to your e-mail address (the sender) |
| © 2000 HOME | Tutorials | [email protected] | Back to Internet 101 |